

Cosmox Blogs
Facial Recognition: The Future of Identification
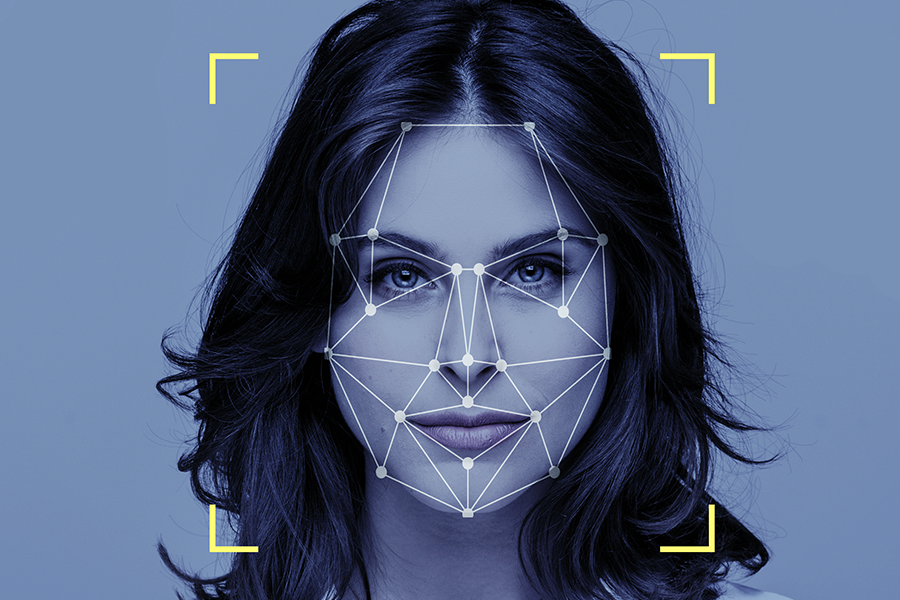
Facial recognition, is a type of biometric software you use in your daily lives, sometimes, without even knowing. You might use it when you unlock your phone, or tap into your office’s building. You might not think much of it as it scans your face and beeps with a little unlocked symbol on the screen before letting you in. The mechanism might look simple in your eyes, but in reality, behind that shiny, glass screen, there are a series of mechanisms and algorithms that perform at an accelerated rate before letting you in. Facial recognition is a concept of biometric software that uses digital geometric maps of a specific individual’s facial features, anomalies, and uniqueness to identify them.
Essentially, facial recognition maps out a person’s facial features to identify them. This geometric map of the face eventually gets translated into a mathematical formula and is stored as a faceprint. The software mainly utilizes artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning to execute this complex and sophisticated process. As your face is scanned, the algorithm identifies your face alongside digital data, images, and videos to verify you as an authorized individual. Facial recognition, in essence, is a very sophisticated and important biometric identification utility for security and identification verification because the entire process occurs without having to make contact.
Although there are many other biometric identification technologies such as the fingerprint, palm/iris detection, etc, facial recognition is well preferred because of its contactless nature, but it comes with a major flaw. While fingerprint and palm detection are all contact forms of biometric technology, they have an increased accuracy, but facial recognition has a considerably low accuracy in recognizing individuals. The reason for the lower accuracy rate is usually because of varying resolutions, illumination of the individual’s face, accuracy-efficiency trade-off, et cetera.
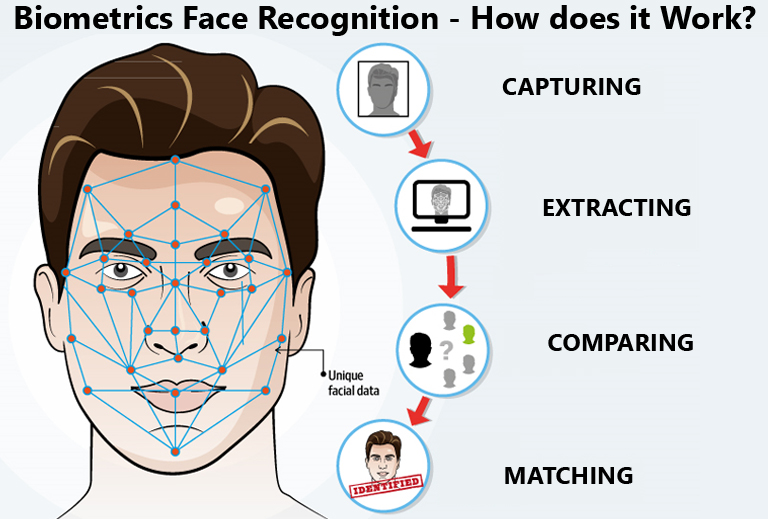
Facial recognition, essentially works in four foundational steps, in detail, these are:
-> Detection: The first and foremost step in which the process of facial detection occurs. The software starts off by identifying a human face in the photo, video, or LIVE video by using a process called computer vision. Computer vision is a field of study in the encompassing topic of Artificial Intelligence (AI) which allows computers to be able to extract and identify data and information from images and videos.
-> Analysis: The next step in the process of facial recognition is analyzing the identified human face in the input. The computer algorithm analyzes the face in detail, in its goal is to identify nodal points, unique features, and defining features in the face. Nodal points are key reference points on a person's face used to measure various facial features. For example, a nodal point is the distance between both your eyes, the length of your nose, or even the depth of your eye sockets. The average facial recognition software identifies approximately 80 nodal points on an individual’s face.
-> Faceprint Storage: This is the next step of facial recognition. Faceprint storage is when the captured and analyzed nidal points are stored in a database. This database also will contain other captured faces as faceprints. Faceprints are unlike images, they represent data as a mathematical formula or a combination of numbers in which they can be identified by the software. Think of it as labeling the person’s face.
-> Recognition: The final step in the facial recognition process is known as recognition, during which the unique faceprint generated from an individual's facial features is analyzed and compared to a comprehensive database. This database contains data collected from faces captured in images or videos, allowing the system to identify or verify the person by matching the faceprint to the stored records.
Facial recognition has been known to be very reliable due to its many benefits as there isn’t a necessity to store passwords, make contact with the device, et cetera but when a large scale test was run by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), multiple algorithmic biases were identified. Many of the biases had originated mainly from demographic imbalances, biological differences, and even built-in physics. The biases within demographic imbalances included the higher false positive rate among West and East Africans compared to East Asian individuals, as the computer failed to recognize their differences due to the lack of training data. In contrast to this, Eastern Europeans had a significantly lower false positive rate as they made up most of the training data. Sometimes, biological differences like skin color affect the computer’s accuracy due to the physics of lighting. Some skin tones reflected light better than other skin tones, making it difficult for the software to identify nodal points.
Facial recognition technology has been increasingly popular as companies are actively trying to eliminate these algorithmic biases and breaches. A few examples of facial recognition technologies include: Amazon (Recognition), Apple (Face ID), and British Airways (Who use facial recognition for passengers boarding flights from the US). Travelers can have their faces scanned instead of needing to show staff their passports or boarding passes.), Cigna (US based healthcare insurer. Cigna allows customers from China to provide a photo instead of using signatures to limit fraudulent activity,), Facebook (Facebook had begun using facial recognition in the US in 2010 as to automatically tag people in photos.), Snapchat (Snapchat allows users to use facial recognition to apply filters that mould to the user’s face.), and many more.
Facial recognition, despite its lower accuracy compared to other biometric technologies, has sustained itself and increased its accuracy. Companies that offer facial recognition services have reduced 10% of anomalies to less than 1% in almost less than 3 years. Facial recognition does offer many benefits such as reduced crime, increased security, eliminating stop and search bias (Mainly British), increased convenience and efficiency, enhanced processing, and integration with a wide variety of technologies.
Although there are many advantages to facial recognition software, there are also multiple disadvantages to consider. These include: supposed breaches of privacy, scope for error, and massive data storage. Many people believe that the use of facial recognition software would eventually restrict and strip them of their freedom, while others believe that it could eventually become a breach of privacy. Facial recognition, no matter how sophisticated the technology is, has a wide scope for errors. This is because, in 2018, Amazon’s facial recognition technology was reported to have falsely identified 28 members of the US Congress as convicted criminals. This goes to say that even a slight change in the camera angle, the difference in hairstyle, or even the application of cosmetics could lead to error and failure and/or misidentification of the individual.
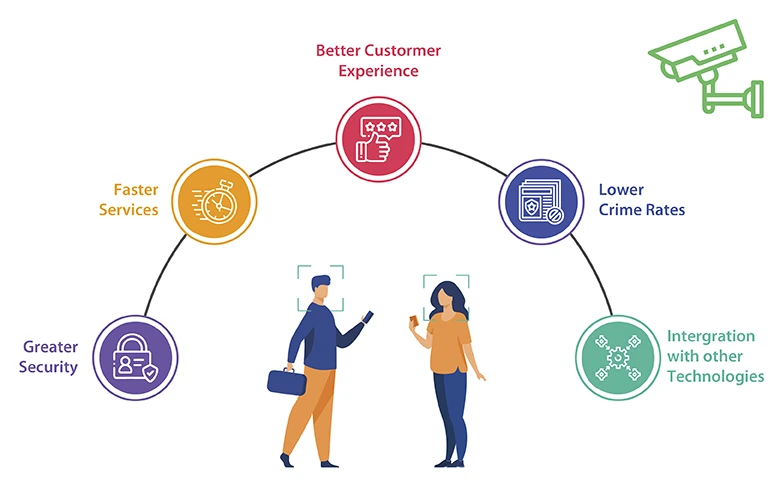
Due to the effective and contactless nature of facial recognition, it has countless applications in multiple industries such as criminal identification of suspects, digital onboarding of clients, access control, security and surveillance, fraud prevention, event registrations, airport operations, financial services verification, smartphone unlocking, retail analytics and et cetera.
In conclusion, facial recognition is a highly sophisticated, biometric technology that is able to identify individuals with complex computer visions, artificial intelligence, biometrics, analysis, and technologies. It is used in many industries for its effectiveness.

Cosmox Blogs
A non profit organization that works on writing and delivering blogs on cosmology, natural sciences & environment, so that people can learn more about it. We even run a forums page, where our users interacts with each other and discuss about Cosmology, Natural Sciences & Astronomy. We even run an instagram and a youtube channel with podcasts.