

Cosmox Blogs
Electromagnetic Waves in the Modern World
"In every ray of light, there is a story of the universe."
From communication to revolutionizing technology and even powering medical solutions, the invisible thread of electromagnetic waves are the base stone shaping the future and present alike. This article explores the origin, properties as well as the role of them in influencing the world around us.
Electricity can be static and so can Magnetism. A changing magnetic field will induce a changing electric field and vice-versa—the two are linked. These changing fields form electromagnetic waves. Unlike mechanical waves, they do not require any energy to travel.

Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the entire distribution of electromagnetic waves according to frequency or wavelength. Although all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, they do so at a wide range of frequencies, wavelengths, and photon energies. The picture below shows the detailed classification of waves in the spectrum.
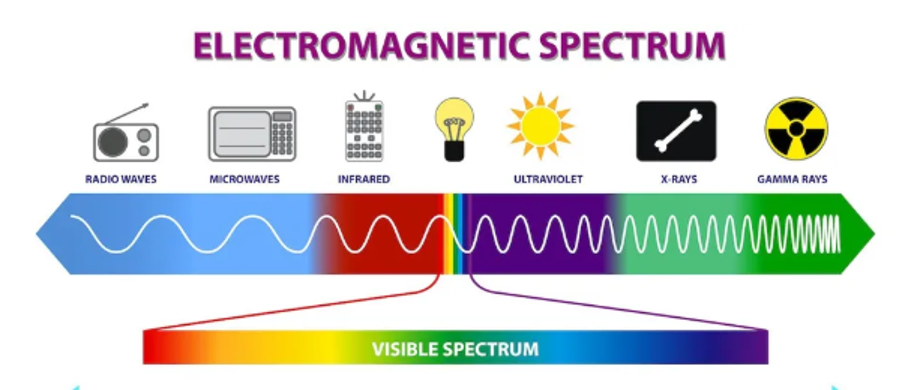
Waves across various spectrums help us study different objects in the Universe. For example- Radio waves and microwaves, which have the lowest energies, allow scientists to pierce dense, interstellar clouds to see the motion of cold gas. The gamma rays with the highest energy help us study supermassive black holes and neutron stars while also being used in the medical field.
Application in Communication
The most common wireless technologies use electromagnetic wireless telecommunications, such as radio or infrared signals. With infrared waves, distances are short (such as a few meters for television remote control). In contrast, radio waves can reach as far as thousands or even millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications.
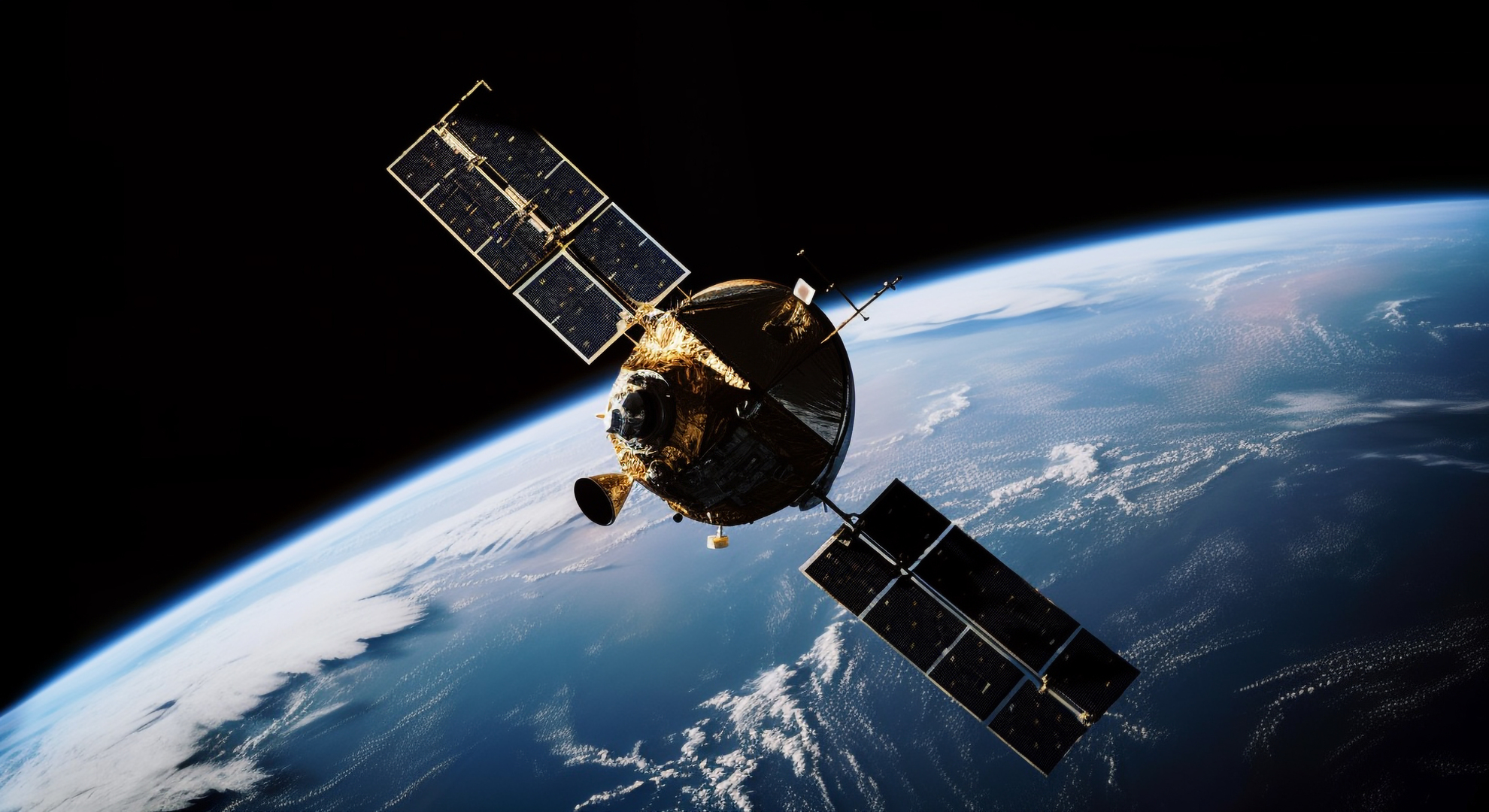

1) A radio wave communication system is a system that uses radio waves to transmit and receive information. They are used for a wide variety of communication applications, including radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, cellular phone networks, and satellite communications. A typical radio wave communication system consists of the following components:
-> Transmitter: The transmitter generates the radio waves and transmits them to the receiver.
-> Antenna: The antenna radiates the radio waves from the transmitter into the air.
-> Receiver: The receiver receives the radio waves from the transmitter and decodes the information contained within them.
This system has various applications in the modern world.
-> These are used in the transmission of TV signals, FM and AM signals, telecommunication signals, and GPS.
-> They are used in Bluetooth connectivity, and WiFi connectivity for providing internet.
-> It is used in signal transmission.
-> Used in radio-controlled toys
2) Satellite communications rely on the transmission of EM waves, primarily in the microwave and radio frequency bands, to establish global communication networks. Satellites, positioned in various orbits around the Earth, receive and transmit signals to and from ground stations
-> Environmental monitoring: Satellites can be used for environmental monitoring and map making
-> Navigation: Satellites like GPS use radio time signals to help mobile receivers determine their location
-> Weather forecasting: satellites permanently observe the Earth's atmosphere, allowing for a flow of information on weather trends, amount of precipitation, temperatures, and other parameters related to the environment.
-> Disaster Management - Satellites constitute a critical aspect of disaster response operations and emergency management. Satellite imagery and data during natural disasters such as Earthquakes, floods, or hurricanes may mirror the geographical damage that may be caused in real-time, enabling emergency response teams to set aside their resources more precisely based on the information to organize relief efforts
3) Optical Fibre- The term 'optical fiber communication' refers to a communication technique in which a signal is transmitted as light, with optical fiber serving as the medium for moving those light signals from one location to another. A signal transmitted through an optical fiber is transformed from an electrical signal into light, which is then converted back into an electrical signal at the receiving end. This enables very high-speed communication as data travels at the speed of light.
Application in the Medical Field
Electromagnetic waves have transformed the medical field, enabling innovative techniques for treatment, monitoring, and research. Their applications range from advanced therapeutic technologies to precise biomedical communication systems
1) Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a minimally invasive procedure that uses radiofrequency waves to heat and destroy tissue, tumors, or other growths in the body. It can be used to treat a variety of conditions, including - Tumours, abnormal heart rhythm, and more.
2) X-rays are made by using electromagnetic waves to produce images of the body, its organs, and other internal structures for diagnostic purposes. X-rays pass through body structures onto specially-treated plates (similar to camera film) or digital media and a "negative" type picture is made (the more solid a structure is, the whiter it appears on the film).
3) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive imaging technology that produces three dimensional detailed anatomical images. It is often used for disease detection, diagnosis, and treatment monitoring.
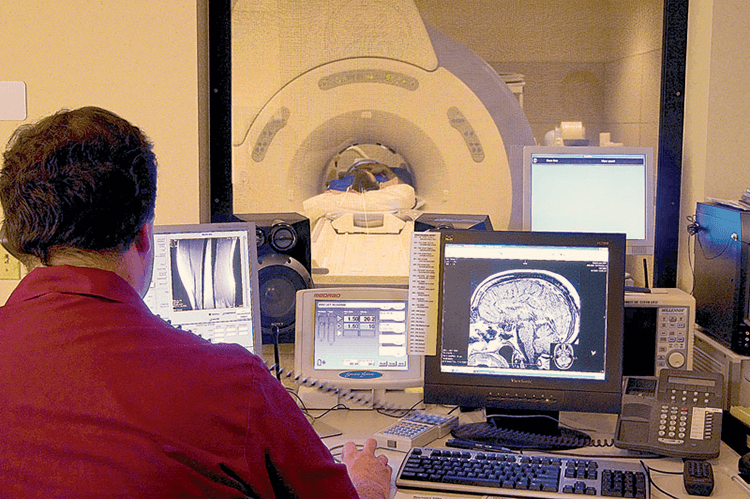
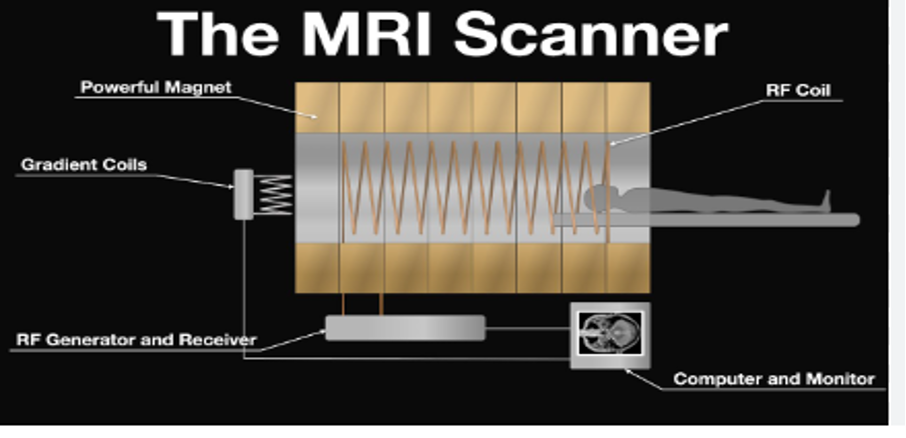
MRIs employ powerful magnets which produce a strong magnetic field that forces protons in the body to align with that field. When a radiofrequency current is then pulsed through the patient, the protons are stimulated, and spin out of equilibrium, straining against the pull of the magnetic field. When the radiofrequency field is turned off, the MRI sensors are able to detect the energy released as the protons realign with the magnetic field. The time it takes for the protons to realign with the magnetic field, as well as the amount of energy released, changes depending on the environment and the chemical nature of the molecules. Physicians are able to tell the difference between various types of tissues based on these magnetic properties.
4) Gamma knife Radiosurgery - Gamma Knife uses very precise beams of gamma rays to treat an area of disease (lesion) or growth (tumor). It’s most often used in the brain. The beams of gamma radiation send a very intense dose of radiation to a small area without a need to make an incision. Radiosurgery destroys cells so that they can’t grow. A lesion or tumor will shrink in size over time.
Other applications
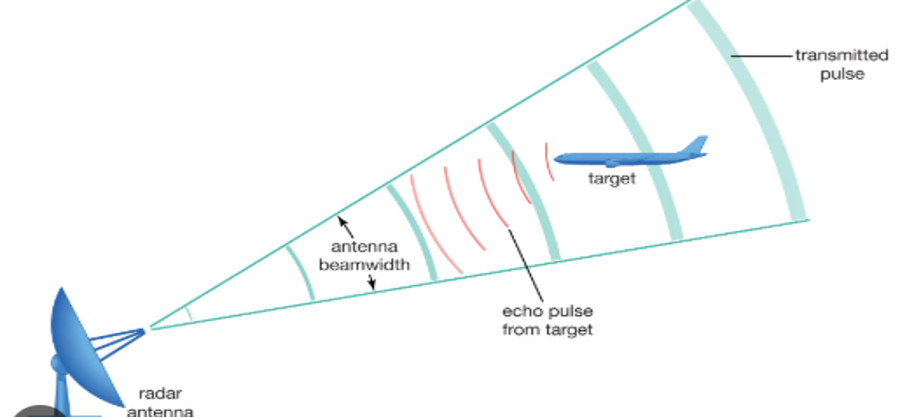
1) Radar -The word radar comes from the acronym radio detection and ranging. As the name implies, radars use radio waves to determine the distance and velocity of the targets they hit. A radar system usually consists of a transmitter to send out radio signals and a receiver to catch any reflected energy from targets. How does the Radar work?
-> The antenna acts as a transmitter that sends radio waves through the air.
-> Radio waves hit the target object or airplane and reflect back.
-> The antenna picks up reflected waves during breaks between transmissions. The same antenna acts as both transmitter and receiver.
-> The duplexer switches the antenna to the receiver.
-> There is a computer present in the receiver which processes reflected waves and displays them on a screen.
-> The target plane can be shown on screen with any other nearby targets.
Radar is widely used in air traffic control, marine navigation, missile defense, and other important fields.
2) Solar Technology - UV solar technology refers to the development of solar cells that can capture and convert ultraviolet light into usable energy. This technology leverages materials that are sensitive to UV light, allowing solar panels to harness a broader spectrum of sunlight. By incorporating UV-sensitive materials, these advanced solar cells can significantly increase the overall efficiency of solar energy systems
Future Prospects
The future of electromagnetic waves holds immense possibilities, driving innovation in communication, healthcare, space exploration, and beyond. Given below are the two most important upcoming technologies that will revolutionize the modern realms.
1) 6G is the sixth generation of wireless technology, and it's expected to be available in the early 2030s. 6G will offer faster speeds, lower latency, and higher capacity than previous generations of mobile networks.6G speed is expected to be 100 times faster than 5G with enhanced reliability and wider network coverage.

It's expected that 6G wireless sensing solutions will selectively use different frequencies to measure absorption and adjust frequencies accordingly. This method is possible because atoms and molecules emit and absorb electromagnetic radiation at characteristic frequencies, and the emission and absorption frequencies are the same for any given substance.
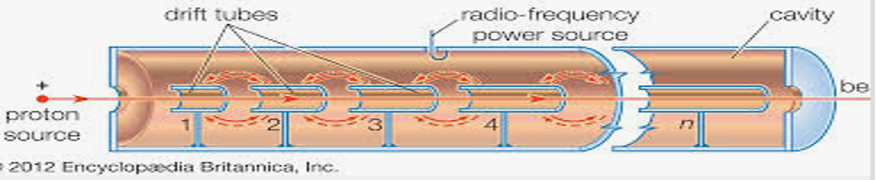
2) Particle accelerators use electromagnetic waves to propel charged particles to high speeds, enabling discoveries about the universe's fundamental structure. They are vital in medicine, such as proton therapy for cancer, and industrial applications like material testing. Despite their significance, accelerators are still evolving, with research aiming to create smaller, energy-efficient models for broader accessibility. Future developments could revolutionize clean energy, advanced material science, and space exploration, solidifying their role as critical tools for scientific progress and technological innovation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electromagnetic waves are essential in shaping our world, and driving advancements in communication, healthcare, energy, and technology. Their versatile nature and endless applications make them a base of modern innovation. As research continues, electromagnetic waves will unlock even greater possibilities, transforming the way we live and interact globally.

Cosmox Blogs
A non profit organization that works on writing and delivering blogs on cosmology, natural sciences & environment, so that people can learn more about it. We even run a forums page, where our users interacts with each other and discuss about Cosmology, Natural Sciences & Astronomy. We even run an instagram and a youtube channel with podcasts.